Black Hat USA 2025 is here, and one theme looms larger than ever: the weaponization of artificial intelligence. For years, defenders have leveraged AI for anomaly detection, automated response, and threat intelligence, but this might be the year when offensive AI takes center stage. The cybersecurity landscape has undergone a fundamental shift, and the balance of power is teetering on the edge of disruption.
You’ve likely noticed the growing sophistication of attacks over the past couple of months. The cybersecurity community is witnessing an unprecedented arms race, with artificial intelligence as the new battlefield. While defensive AI solutions have matured considerably, their offensive counterparts have evolved in the shadows, and now they’re stepping into the light.
Are you ready for a world where AI doesn’t just defend your systems but actively works to compromise them? If you’re in Vegas for Black Hat, understanding offensive AI won’t just be interesting; it will be essential for your organization’s survival strategy.
Defining Offensive AI: The Attacker’s New Advantage
What exactly is offensive AI? At its core, offensive AI refers to machine learning or generative models deliberately used to power or enhance cyberattacks with precision, scale, and evasion capabilities that far exceed traditional methods. Unlike its defensive counterpart, which works to identify anomalies and protect systems, offensive AI actively seeks to circumvent security measures and exploit vulnerabilities.
The contrast with defensive AI is striking. While security vendors have spent years developing AI for threat detection and response, offensive AI flips the script by turning these same technological advances against defenders. Think of it as the difference between a shield and a sword; both leverage similar metallurgical principles, but with entirely different purposes and effects.
This is just the beginning. As we move through 2025, offensive AI is rapidly becoming the cornerstone of advanced persistent threats rather than merely an experimental technique.
3 Key Threat Vectors Enabled by Offensive AI
1. LLM-Powered Social Engineering: The Perfect Impostor
Large language models have revolutionized social engineering attacks by enabling threat actors to craft messages that are virtually indistinguishable from legitimate communication. Unlike traditional phishing attempts with their telltale grammar issues and generic phrasing, LLM-powered attacks analyze and replicate specific communication patterns of targeted individuals or organizations.
Do you think your team would recognize an email that perfectly mimics your writing style, references recent projects you’ve discussed privately, and arrives with contextually appropriate timing? The statistics suggest otherwise. Around 82.6% of phishing emails now include some AI-generated content.
Business email compromise (BEC) attacks have been particularly transformed by this technology. By training on compromised email accounts, offensive AI systems can now:
- Analyze communication patterns between executives and finance teams
- Identify optimal timing for fraudulent payment requests
- Craft messages that mirror internal shorthand and terminology
- Respond to questioning in real time with contextually appropriate answers
2. Synthetic Identity Generation: Digital Ghosts That Seem Real
The creation of entirely synthetic yet convincing digital identities has emerged as one of the most concerning applications of offensive AI. Using generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models, threat actors can now produce deepfakes and clone voices with frightening accuracy, enabling impersonation attacks that bypass traditional identity verification methods.
These synthetic identities aren’t just static images or one-off voice samples. They’re increasingly becoming fully realized digital personas with:
- Consistent visual identities across multiple generated images
- Voice profiles that maintain consistent speech patterns and accents
- Social media histories that are generated retroactively to establish legitimacy
- Employment backgrounds that withstand surface-level verification
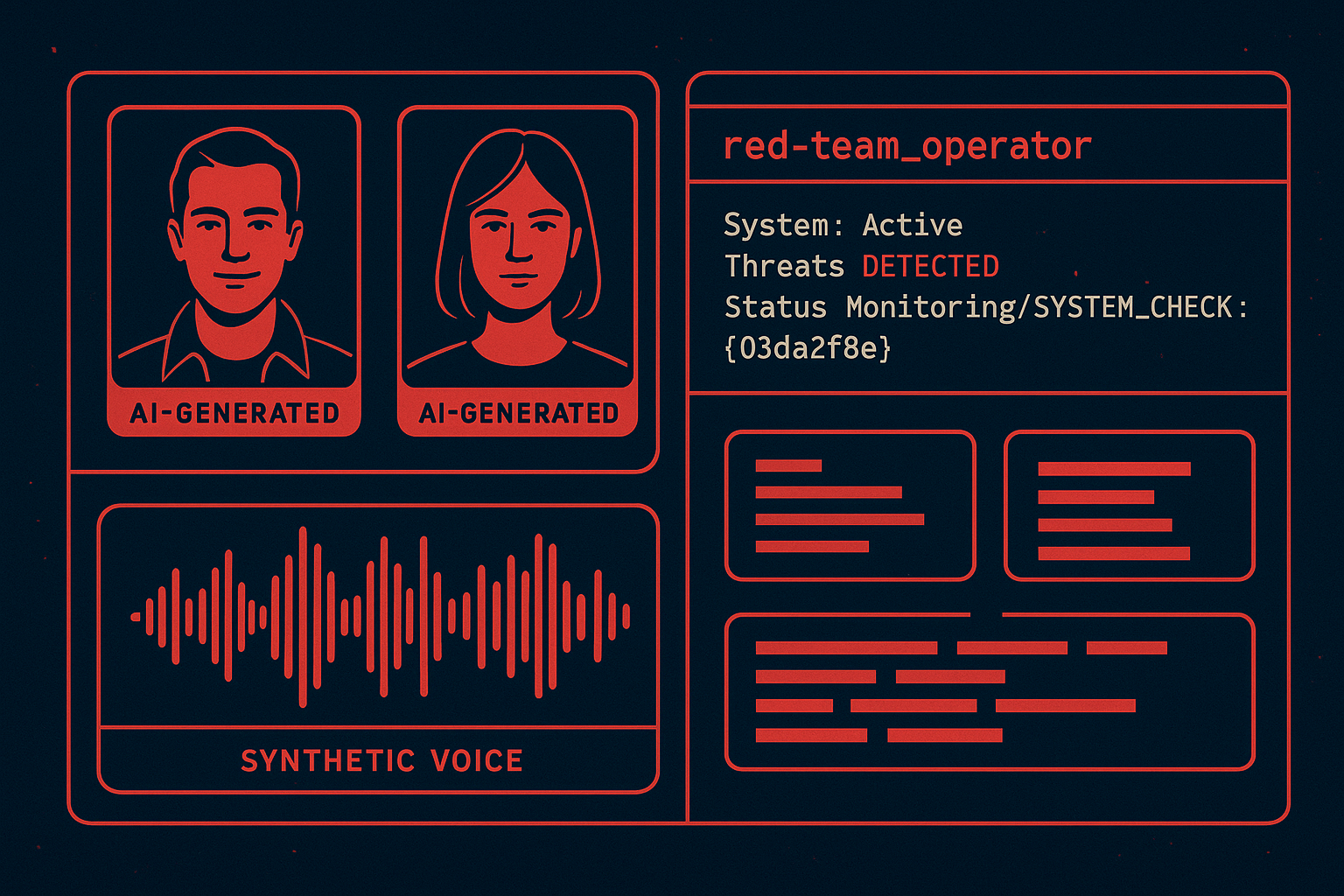
Model Extraction and Jailbreak Attacks: Turning AI Against Itself
Some 78% of CISOs say AI-powered threats significantly impact their organizations, up 5% from 2024. Perhaps the most technically sophisticated offensive AI techniques involve targeting AI systems themselves.
Model extraction attacks attempt to reverse engineer commercial AI models by systematically probing their responses, while jailbreak attacks exploit weaknesses in content filtering and safety measures.
These attacks have serious implications:
- Security companies that rely on proprietary AI models risk having their intellectual property stolen.
- LLM-based security controls can be circumvented through carefully crafted prompts.
- Defensive AI systems can be manipulated to generate false negatives through adversarial techniques.
- Cloud-based AI services can be used as unwitting accomplices in attacks.
A particularly concerning trend involves attackers exploiting transfer learning techniques to quickly adapt general-purpose models for malicious purposes. By fine-tuning models on security exploit databases, threat actors can create systems that suggest novel attack vectors or automatically generate customized malware variants that evade signature-based detection.
How Red Teams Are Using Offensive AI: Ethical Offense
Forward-leaning security teams aren’t just bracing for offensive AI—they’re deploying it. Red teams and penetration testers are now embedding AI into their operations to emulate advanced adversaries more accurately and test the resilience of their organizations under realistic, AI-driven attack scenarios.
Recent red team exercises have highlighted the growing power and precision of offensive AI tools. In controlled environments, AI-enabled red teams have successfully:
- Auto-generated spear phishing campaigns tailored to corporate language and tone, harvested from internal comms and social media
- Created synthetic voice deepfakes of C-level executives for real-time vishing and impersonation attacks
- Deployed polymorphic malware, dynamically mutating payloads to bypass endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools
- Used AI to automate lateral movement, analyzing network topology, and making decisions about privilege escalation paths in real time
These tactics aren’t theoretical—they’re being tested and refined by red teams across industries. The ethical use of offensive AI enables defenders to anticipate what AI-powered threat actors will do next.
The growth in offensive deepfake usage illustrates the urgency. Deepfake-based content (commonly used in fraud, impersonation, and social engineering) is projected to surge from 500,000 in 2023 to over 8 million by 2025, signaling a dramatic escalation in attack surface and realism.
As these tools evolve, so must the ethics. Security teams leveraging offensive AI must tread carefully, ensuring transparency, consent, and strict scoping to maintain trust while sharpening defenses.
Blue Team Response: Defending Against Offensive AI
As offensive AI capabilities expand, blue teams must adapt their defensive strategies accordingly. Traditional security approaches that rely on static signatures or simple anomaly detection are increasingly insufficient against these dynamic threats.
Next-generation AI-based defenses are evolving to meet these challenges through:
- Behavioral analytics that establish baseline communication patterns to flag anomalies
- Multimodal authentication that combines multiple verification factors
- Adversarial training that helps defensive AI recognize manipulation attempts
- LLM content detectors that identify machine-generated text
Particularly promising are defensive systems that incorporate adversarial machine learning techniques. These systems are continuously trained against potential attack methods, making them more resilient to manipulation. Some cutting-edge approaches include:
- Generative adversarial networks that produce potential attack examples to improve detection
- Reinforcement learning from human feedback that incorporates security analyst insights
- Transfer learning that applies knowledge from known attacks to identify novel variations
- Explainable AI systems that help analysts understand why specific alerts were generated
Despite these advances, human oversight remains critical. Blue teams are increasingly adopting collaborative approaches where AI handles initial detection and triage while human analysts focus on strategic response and contextual understanding.
What to Expect at Black Hat USA 2025
Black Hat USA 2025 will be the premier showcase for offensive AI content. On August 5, the AI Summit takes center stage—a dedicated day of keynotes, panels, and technical workshops dissecting both generative and adversarial AI in offense and defense. Anticipate deep dives into AI agent exploitation, model-jailbreaking techniques, and real-world offensive workflows.
In the main Briefings (August 6–7), expect at least a handful of AI-focused talks under the “AI, ML & Data Science” track. One specifically highlights “Offensive Operations” with Hariharan Shanmugam, offering firsthand insights into AI’s role in red-teaming. Meanwhile, Arsenal and Arsenal Lab (Aug 6–7) provide hands-on environments for testing offensive AI tools, with researchers bringing open-source exploits, adversarial‑AI scripts, and LLM fuzzers for interactive demos.
Attendees can experiment, collaborate, and reverse engineer emerging offensive AI toolchains in real time.
Key Players and Vendors to Watch
A number of vendors are spotlighting offensive AI as their core pitch:
- Protect AI, title sponsor of The AI Summit, is anchoring the conversation around agent‑level AI threats and model exploitation.
- At the Business Hall, platinum-level players like Trend Micro, Microsoft Security, Elastic, Lockheed Martin, and World Wide Technology will demo how reflexive AI tools both target and detect generative attacks.
- Innovative startups like Mindgard (booth #6227) will highlight “automated AI red‑teaming” and runtime LLM offensive testing capabilities.
- Look out for sponsored sessions such as “Future Threats: How Agentic AI and Lab‑Born Exploits Are Outpacing Today’s Defenses” (by Brian Black), signaling how threat actors leverage self-learning AI & emergent exploit stacks.
Beyond vendors, the advisory board for The AI Summit—featuring heavyweights like Microsoft’s Tori Westerhoff, MITRE’s Jyotirmay Gadewadikar, and Kudelski’s Nathan Hamiel—will guide the discourse, bringing blue‑team and red‑team perspectives natively into AI strategy sessions.
Predictions: Will This Be the Year Offensive AI Goes Mainstream?
All signs point to yes. In 2025, Black Hat is embedding offensive AI deep into its core, not relegating it to a novelty track. With a full summit, AI‑labeled breakouts, Arsenal demos, and heavy sponsor alignment, the conference has officially moved generative and agentic AI into the mainstream cyber battleground.
Sponsored keynotes from Fortinet—revealing real‑world jailbreaking of AI tools integrated into malware—to Brian Black’s session on lab‑born exploits, signal that both red and blue sides will detail offensive AI.
Preparing Your Organization for the Offensive AI Era
As offensive AI reshapes the cybersecurity landscape, organizations must take proactive steps to prepare their defenses and security teams. This isn’t just about buying new tools; it requires a fundamental shift in security strategy and mindset.
Making the leap to an AI-resilient security posture demands a fundamental shift in strategy and mindset. Security leaders must begin by mapping their organization’s unique exposure to offensive-AI tactics, posing hard questions such as:
- How vulnerable are employees to context-rich social-engineering lures?
- What multi-factor verification checks protect sensitive communications or high-value transactions?
- To what degree do current defenses lean on static pattern matching versus adaptive behavioral analytics?
- And, critically, which in-house AI systems could attackers manipulate or extract?
Technology alone, however, cannot shoulder the burden. A parallel track of human readiness is essential. Teams need training that demystifies offensive-AI capabilities, hones their ability to spot synthetic media and generated text, and updates incident-response playbooks for machine-speed threats.
Regular red-team exercises, powered by the same AI techniques adversaries will wield, transform that knowledge into muscle memory, ensuring defenders can recognize and repel AI-enabled attacks before they metastasize.
Remember that while the tech is changing fast, the basics of security still apply. Multi-factor authentication, principle of least privilege, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring are still key to a strong defense even against AI-powered attacks.
Navigating the New World of AI-Powered Threats
The rise of offensive AI is a paradigm shift in cybersecurity and requires both technological adaptation and strategic rethinking. As Black Hat USA 2025 will undoubtedly demonstrate, we’re entering an era where the line between theoretical and practical offensive AI has not just blurred but disappeared entirely.
Are you ready to defend against attackers using AI as their primary weapon? Will your current security strategies hold up against synthetic identities, LLM-powered social engineering, and adversarial attacks? The organizations that will thrive in this new world will be those that understand these threats and adapt their defenses accordingly.
Make offensive AI a priority on your agenda at this year’s Black Hat. The sessions, demos, and conversations around this topic won’t just be interesting; they’ll be essential to your organization’s security in the next few years.
At IOD, we’re closely tracking the conversations, sessions, and signals around offensive AI and what they mean for cybersecurity teams navigating this shift.
Want to turn these insights into expert-driven content that speaks directly to your technical audience?
Scale your security content.

